AI agents are advanced computer programs that can autonomously perform a variety of tasks, such as decision-making, problem-solving, and interacting with external environments. Unlike traditional automation, AI agents can think, adapt, and act independently without constant guidance.
AI Agents are valuable tools for businesses, allowing them to delegate repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more critical activities. Additionally, AI agents can be utilized in various applications, including software design, IT automation, inbound & outbound calls, and providing notifications and alerts via SMS.
DATA IS KING
When it comes to training AI agents to be effective in an organization "data is king". The effectiveness of AI agents is directly tied to the quality and relevance of the data they are trained on. It is crucial to ensure that the data provided to AI agents is up-to-date and contextually relevant to the organization's operations.
To achieve this, a vector database is recommended for storing and managing the data effectively. Creating and maintaining the database needed to train AI agents is fundamental to the success of AI agents within your organization.
DATA COLLECTION FOR AI AGENTS
Data collection is a fundamental aspect of training AI agents for successful implementation. The process involves building a vector database filled with relevant information about the business, ensuring that the database is continuously updated with real-time data to keep the AI agents contextually aware.
This real-time data includes emails, calendar events, new projects, tasks, hires, leads, and any other interactions within the business. Automations and purpose-built AI Agents are utilized to collect and save this data efficiently.
Effective data collection and database management are crucial components in developing highly efficient AI agents. Advancements in automating and streamlining the process, ensure scalability, sustainability, and effectiveness in keeping the agents up to date without manual intervention.
PROMPT ENGINEERING
Prompt engineering is essential for developing effective AI agents. It involves structuring prompts, providing context, clear instructions, and output requirements. Examples play a vital role in training the agents to perform tasks accurately.
PROMPT GRIFTERS
We've seen the marketplace inundated with grifters aiming to capitalize on the fear of missing out prevalent in the tech industry. These hastily packaged AI prompts and "turnkey" automated solutions add little substantial value. These grifters flood the marketplace with informational products that lack depth and fail to meet the needs of customers. Their focus on quick profits rather than genuine innovation results in a saturation of low-quality offerings, ultimately diminishing the overall quality of AI solutions available.
ENGINEERED ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
The strength of the prompt plays a significant role in the agent's performance. If the prompt is weak, the agent may fail to work at all. On the other hand, even with a seemingly successful agent, there is a risk of it breaking or under-performing when faced with unforeseen scenarios or edge cases. This highlights the importance of outlining prompts clearly and accounting for various possibilities.
To facilitate prompt engineering, a template is often used. This template includes an objective, providing a broad overview of the agent's role. Context is then provided to specify details such as whose inbox the agent is managing and the types of emails it receives. Clear instructions are given on how to perform the job, similar to how one would provide instructions to a human employee. Additionally, output requirements are defined, specifying what the agent should output after completing its tasks.
AI WITH AGENCY
Tools are provided to AI Agents that allow the AI to perform tasks and have agency. Without tools, an AI agent cannot take any action. Tools can be custom workflows or integrations with existing platforms, allowing the agent to interact with various systems and perform a wide range of tasks.
For example, an email actions tool can enable an agent to send emails, mark them as read, or retrieve information about emails. These tools are built within the AI agent platform and can be called upon by the agent to execute specific actions.
Integrations with external platforms provide access to data and actions that the agent may need to complete its tasks. When building an AI agent, it is important to consider the tools and integrations necessary for the agent to have the required capabilities and access to relevant data.
AI TEAM ARCHITECTURE
The biggest challenge organizations face is architecture when building teams of agents. The framework involves breaking down job functions into various workflows. The architecture for building agents involves different agents for each workflow, such as an inbox management agent, lead qualification agent, lead enrichment agent, and lead nurturing agent.
SALES DEVELOPMENT REPRESENTATIVE
A SDR has workflows for prospecting, following up, and booking calls. Each workflow consists of different tasks. Hard automations can automate tasks, but agents are better at reasoning and thinking behind tasks. Specialization of job function and providing the AI team access to other relevant team members provides the most consistent results.
These agents work together to handle different aspects of lead generation. There is no need for an agent group chat or centralized commander. It is important to design the architecture correctly when building a team of agents to replace a job function.
AI LEAD GENERATION TEAM
Specialization of AI agents and giving each individual agent appropriate access to the tools data that needs to complete its work provide the most consistent results when incorporating AI agents and automation into your organization's workflow.
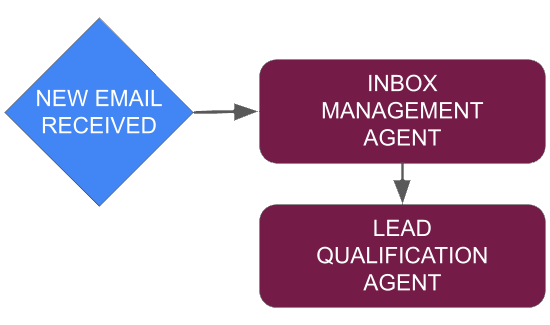
INBOX MANAGEMENT AGENT
This agent is specialized in the management of a designated inbox. This agent is responsible for proper categorization and routing of inbound communication. When properly trained inbox management agent will route inquiries to proper lead qualification or nurturing agent.
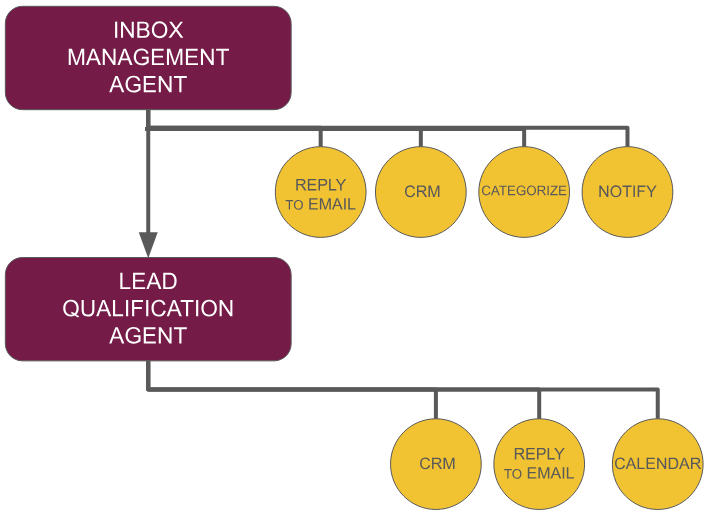
LEAD QUALIFICATION AGENT
This agent is responsible for responding to inquiries and asking information needed to verify potential. Once lead is determined to be qualified the lead qualification AI agent books calendar event based on availability.
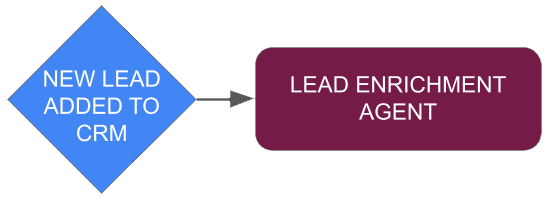
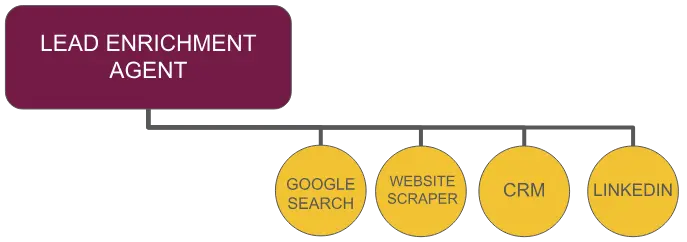
LEAD ENRICHMENT AGENT
The lead enrichment agent is given access to the web and provided with web-scrapping tools needed to obtain all available information on a potential lead and their organization. This specialized individual agent is called upon by other AI agents within the team to ensure the most effective engagement.
Lead enrichment agents are used to assign quality scores to leads to help prioritize action.
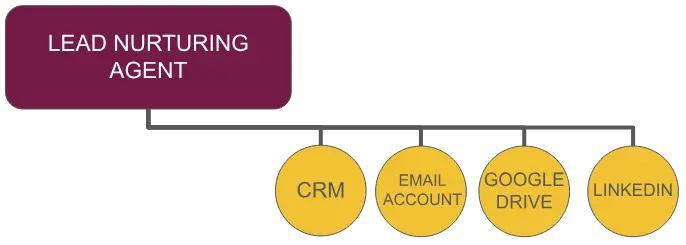
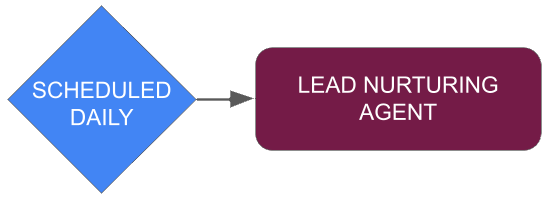
LEAD NURTURING AGENT
This AI agent uses activity from within the CRM to identify leads that have not been contacted and engage with relevant next steps or content that can assist in the customer in the purchasing decision.
This AI agent can be used to identify all leads that have not been contacted within the last 10 days. It will then draft an email, outbound call, or text to provide the potential customer with information most relevant to them. The AI agent can identify potential case studies from within Google Drive for example and provide that as part of it's correspondence.